Call Now
+91 471 2326774
+91 471 2326784
+91 9497 722 774
+91 471 2326774
+91 471 2326784
+91 9497 722 774
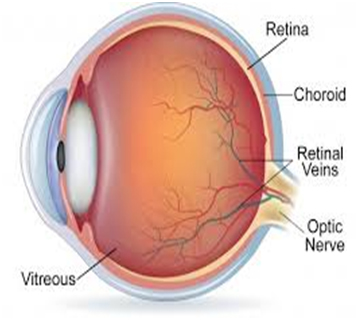
It is the central part of the retina that helps us see details of objects clearly.
The eyes retina has one main artery and one main vein. When the main retinal vein becomes blocked, it is called Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO).When branches of the main retinal vein become blocked it is called Branched Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO).When the vein is blocked blood and fluid spill out into the retina, this can cause the macula to develop swelling and affect central vision. Eventually without blood circulation, nerve cells in the eye can die and vision can deteriorate.
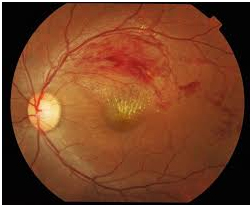
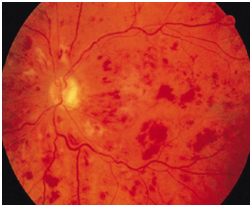
Aim of treatment is to keep the vision stable. For this, leaking blood vessels of the retina should be sealed to prevent further swelling of macula. This can be done either by laser treatment or by using medication that is injected into the eye. In severe cases, both may be required.
There is a clear material, called vitreous gel that fills the eye ball. This is attached to the retina. Due to various factors the vitreous may change shape and pull away from the retina. This can cause a break or tear in the retina. Subsequently vitreous can seep through and lift of the retina in the area, which leads to the retinal detachment.
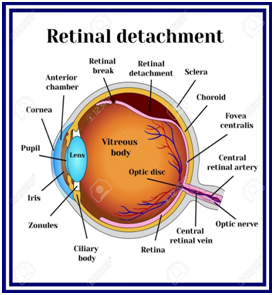
Retinal Breaks -Laser is done around the area of break, in order to seal the retina and prevent detachment.
Retinal Detachment- Surgery is required to place the retina back into it’s original position. It involves replacing the vitreous gel with and oil bubble or a gas bubble and applying laser burns to keep the retina attached. After this surgery a certain head position has to maintained for several days.
This occurs when fluid builds up under the retina causing distorted vision. Affected person complains of,
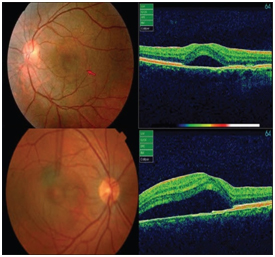
Most cases resolve on its own in 1-2 months. If there is severe vision loss or the fluid leakage is still present, laser treatment or photodynamic therapy may be used. This will seal the leak and restore vision.
This occurs in some premature babies born before 31 weeks of pregnancy. These low – birth weight babies are usually exposed to extra medications, more oxygen, temperature changes, etc, which might affect the development of blood vessels of the eyes. This can cause severe vision problems for the child later on in life. Hence, all premature babies should be examined for ROP by an ophthalmologist.
Infants>28 weeks of age – screening within 4 weeks
Infants<28 weeks of age or birth weight <1200g – screening at 2-3 weeks of birth.
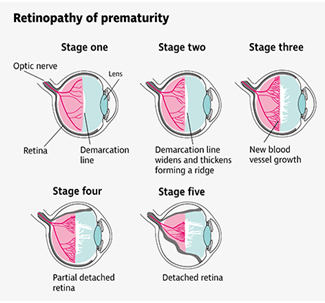
Initially, ROP is monitored to see if it resolves on its own. If abnormal blood vessels continue to grow,it must be treated in one or more of the following ways;
Follow- up period is unpredictable as there can be a recurrence even after 54 weeks of post- gestational age. Hence follow-up should continue till vascularisation is complete and normal.
As babies with ROP grow, they need to be examined regularly for vision problems, such as near sightedness, lazy eye (Amblyopia), squint, detached retina and glaucoma.
It is a complication of diabetes that affects eyes. It is caused by damage to the blood vessels of the retina. There are two main stages :

This is the early stage. It causes the macula to swell causing blurred vision. Also, the blood vessels in the retina can close off causing low blood supply to the macula, thereby affecting vision.
It is the more advanced stage when the retina starts growing new blood vessels. These vessels are fragile, causing them to bleed into the vitreous. With time, if can also lead to retinal detachment, thereby stealing both central and peripheral (side) vision.
Intravitreal drugs used for DR are anti VEGF drugs. These are injected into the affected eye to stop the abnormal blood vessels from growing and also help control the leaking blood vessels. This is highly effective in preserving central vision. However, patients may require two or three injection in consecutive sittings, depending on the leakiness of the blood vessels.
Commonly used intravitreal drugs are;
An alternative to these is an intravitreal dexamethazone implant (Ozurdex) which is used in patients with diabetic macular edema refractory to multiple anti VEGF injections.
Anti VEGF treatment should not be given to those who are allergic to anti VEGF , if there is an infection in the other eye or severe infection elsewhere in the body, and also in pregnant or breast feeding women. It is to be used with caution in patients with a history of heart attack or stroke in the last six months and also in those with uncontrolled high blood pressure.
Laser procedure – This helps seal off leaking blood vessels and reduces swelling of the retina. It also prevents from growing again. This is usually done in 2 to 3 sittings.
Surgery – is indicated in advanced DR when there is bleeding into the vitreous or there is traction/pull on the retina from the scar tissue, causing detachment of retina.
Screening of DR
People with type 1 diabetes- Annual examination for DR from five years after onset of diabetes.
People with Type 2 diabetes – examination for DR at the time of diagnosis, then yearly examination thereafter.
Women who are develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy do not require an eye examination. However, diabetics who became pregnant should be examined soon after conception and early in first trimester of pregnancy.
Recommended follow-up is every 4-12 months for no retinopathy or moderate NPDR and every 1-3 months for severe NPDR.
Leading cause of vision loss in people 50 years or older. This occurs when a part of the retina called macula is damaged.This causes diminution or loss of central vision.
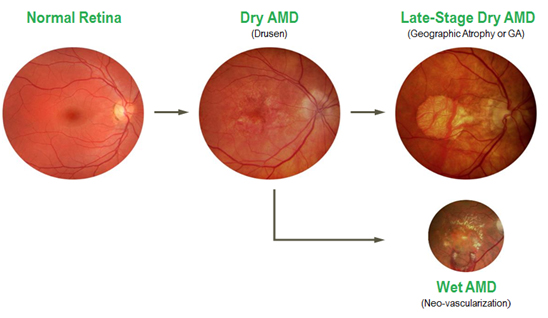
These are of two types of ARMD
Dry ARMD – most common type. The macula becomes thinner with age. Also they develop protein deposits called drusen.
Wet ARMD – less common but more serious. Here, new abnormal blood vessels grow underneath the retina. These may leak blood or fluid causing scarring of macula. This can lead to rapidly progressive loss of vision.
Dry ARMD – As of now there is no treatment for this type.
Wet ARMD – is a treated using medication that is injected into the eye, or by using laser procedure. Both of these will reduce the number of abnormal vessels and decrease their leakage.