Gitanjali Hospital – ENT | EYE | DERMATOLOGY Hospital in Trivandrum
Gitanjali Hospital – ENT | EYE | DERMATOLOGY Hospital in Trivandrum
Vitrectomy
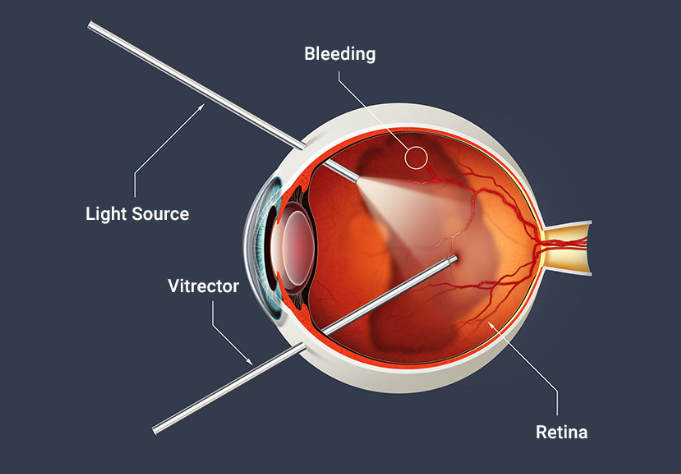
Vitrectomy is a specialized ophthalmic surgical procedure aimed at addressing a variety of serious eye conditions involving the vitreous body, the gel-like substance filling the eye’s interior. Since its inception in the mid-20th century, vitrectomy has evolved into a sophisticated and crucial tool in the field of retinal surgery, offering patients the potential for improved vision and better outcomes in managing complex ocular diseases. In this procedure, small ports are created in the sclera for introduction of the instruments inside the eye. With the assistance of Vitrectomy machines and fine instruments like cutters which deliver high-speed cut rates surgery is performed when the gel vitreous along with membranes proliferated on the retina is removed. For visualization inside the eye we use light probes and to coagulate the retina and retinal blood vessels we use endolaser probes during the surgeries. Other micro instruments and drugs are also used during the surgery which aid in the complete removal of retinal membranes and proliferations on the retina.
For visualization during the surgery which is essential to perform an optimal and complete vitrectomy, we use a special wide-angle lens which is fitted to the higher-end operating microscope which gives a wide angle view of the retina. With the Rapid development of instrumentation for these types of surgeries, we are using smaller gauge instrumentation like 23G; 25G, and 27G instruments where the incision size is reduced to 0.6mm, 0.5mm, and 0.4mm respectively which gives us essentially sutureless surgery with less discomfort to the patient post-operatively. The advantage of smaller gauge instruments is that we can go very close to the retina without much turbulence and tissue damage intraoperatively. These surgeries are called Microincision Vitrectomy Surgeries (MIVS).
The vitreous body is a transparent gel-like substance that occupies approximately two-thirds of the eye’s interior space. It is primarily composed of water, collagen fibers, and hyaluronic acid, which help maintain the eye’s shape and provide structural support to the retina. The vitreous body is critical for light transmission through the eye and plays a role in retinal health by keeping the retina in place against the choroid and sclera.
Indications for Vitrectomy
Vitrectomy is indicated in several severe retinal conditions where non-surgical treatments are insufficient. These conditions include:
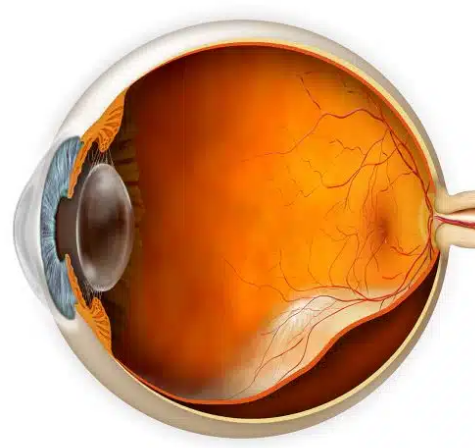
Retinal Detachment: This occurs when the retina separates from the underlying choroid. Vitrectomy can repair the detachment by removing the vitreous gel, reattaching the retina, and sometimes using a gas bubble or silicone oil to hold the retina in place as it heals.
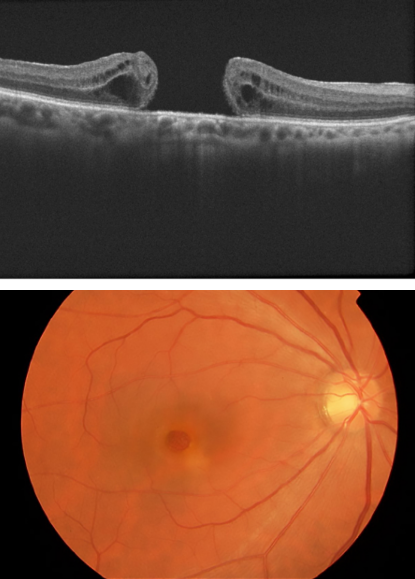
Macular Hole: A macular hole is a defect in the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision. Vitrectomy is performed to remove the vitreous gel pulling on the retina and to encourage closure of the macular hole.
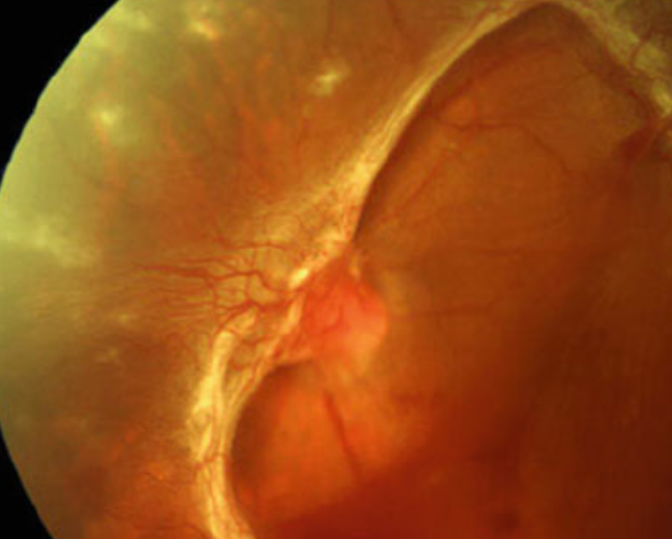
Diabetic Retinopathy: In advanced stages of diabetic retinopathy, the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina can lead to bleeding and scarring. Vitrectomy is used to clear out blood and scar tissue to restore vision and prevent further damage
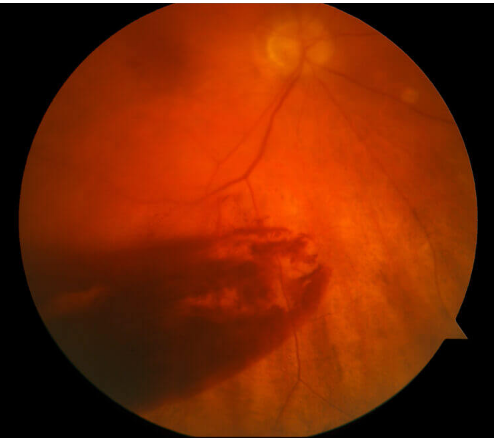
Vitreous Haemorrhage: This condition involves bleeding into the vitreous body, which can obscure vision. Vitrectomy can remove the blood and address the underlying causes of the hemorrhage
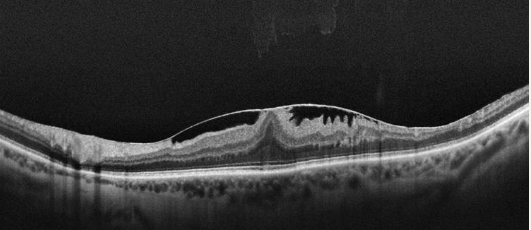
Epiretinal Membrane: This is a condition where a thin layer of fibrous tissue forms on the retinal surface, distorting vision. Vitrectomy can remove this membrane and improve visual outcomes.
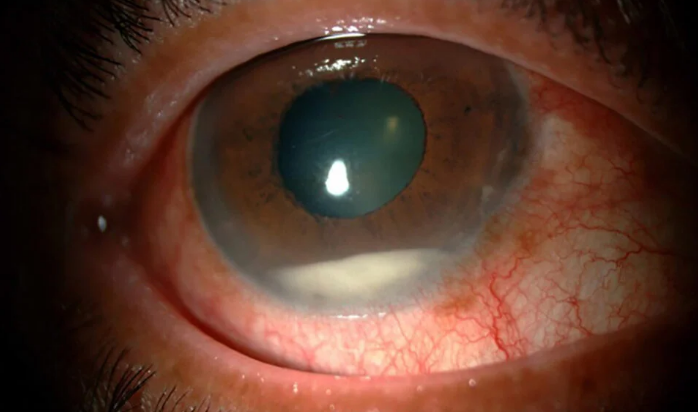
Endophthalmitis- inflammation of the inner coats of the eye, including the vitreous.
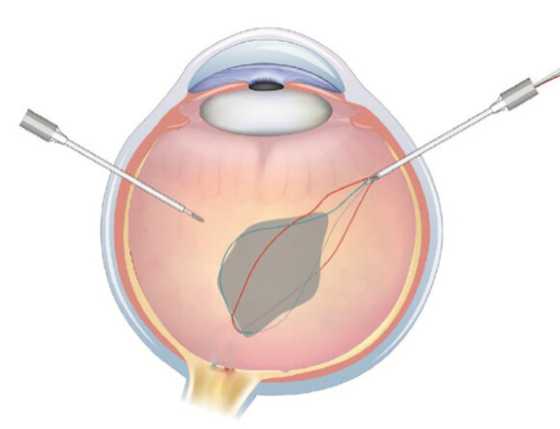
Any intraocular foreign body following trauma.
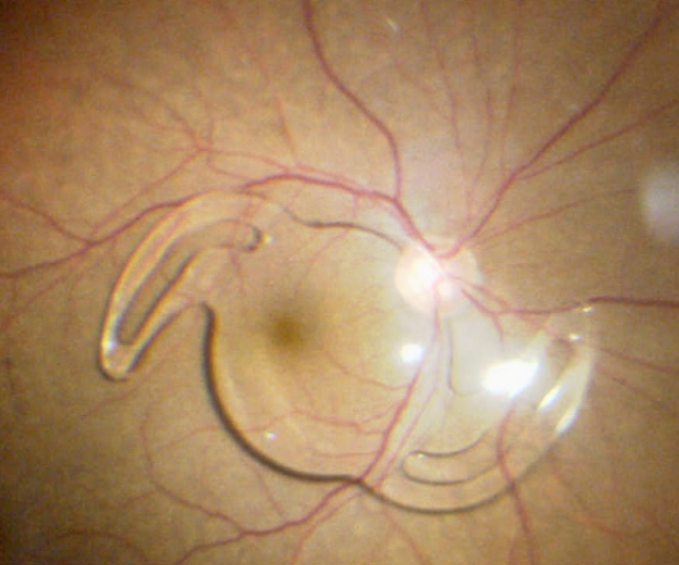
Dislocated lens/ implants
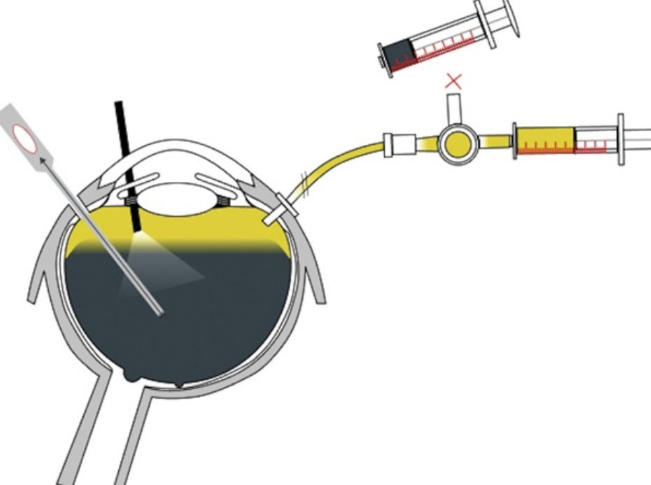
Vitrectomy remains a cornerstone in the treatment of complex retinal conditions, offering hope for vision restoration in cases where other treatments fail.